Significant hair loss affects many women. It’s not only a cosmetic issue, it can also be a sign of an underlying health problem.
In this article, we will clarify the causes of hair loss in women, ranging from natural to serious. We will also review the most effective available treatments and the best methods for hair care.
The Hair’s Life Cycle and Functions
First and foremost, it is important to understand that losing some hair daily is part of its natural life cycle. Hair loss is considered normal as long as it occurs within a reasonable range.
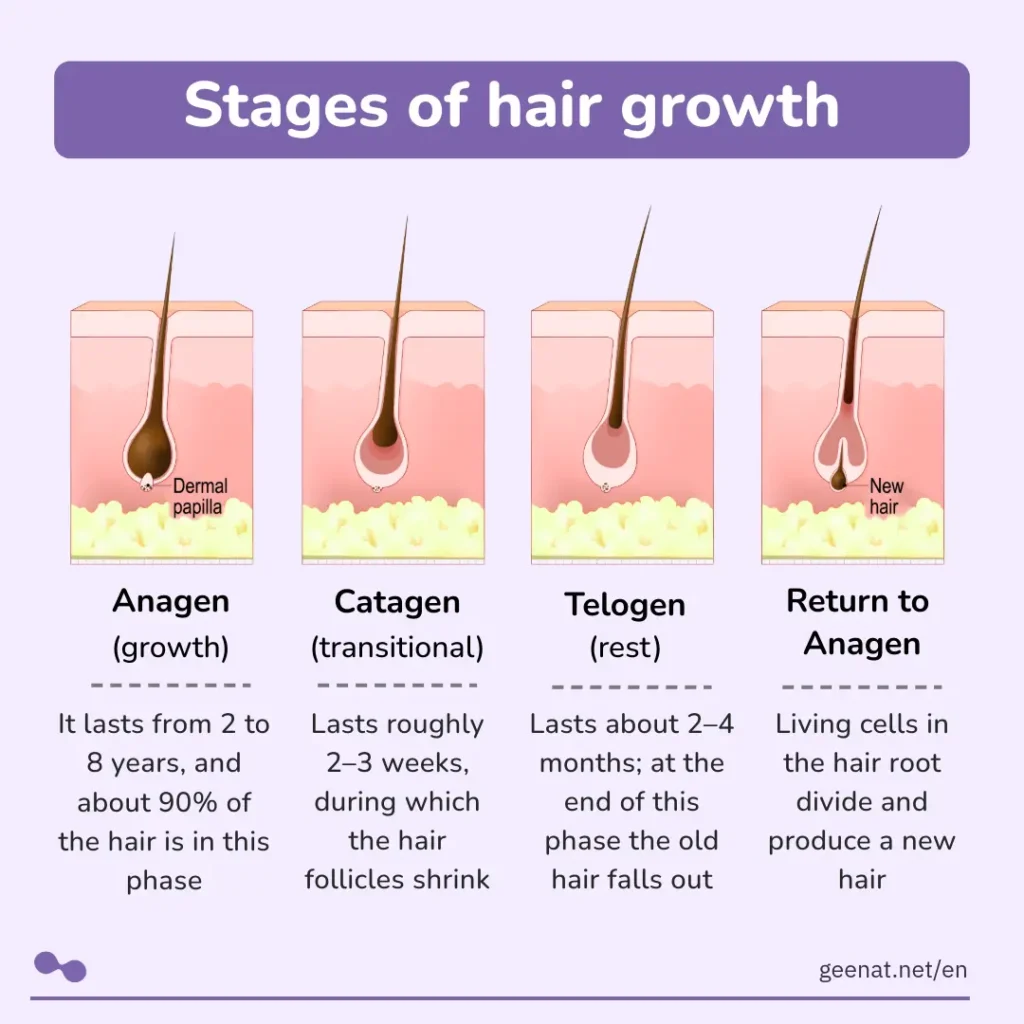
Furthermore, we must appreciate the importance of hair for the human body, particularly for women. This awareness increases our understanding of the need to maintain our hair’s health. In brief, these are the primary functions of scalp hair:
● Protection from ultraviolet (UV) radiation, burns, injuries, and infections.
● Thermoregulation of the body, either by providing insulation in cold weather or by accelerating sweat evaporation and retaining skin moisture in hot conditions.
● Enhancing sensory function, as hair follicles are connected to numerous nerve endings.
● Contributing to social interaction and perceived attractiveness.
● Boosting self-confidence, identity, and self-esteem, given the association of thick hair with femininity in some cultures.
When Does Hair Loss Become Worrisome?
Under normal circumstances, every individual, male or female, loses between 50 and 100 hairs per day. This is a negligible number compared to the approximately 100,000 hair follicles on the scalp.
Therefore, as long as the hair growth cycle continues, shedding this small number of hairs does not represent a significant loss and is not a cause for alarm. This loss is often barely noticeable on our combs, clothes, or floors.
However, some may notice larger amounts of shed hair, areas of thinning, patches of baldness, a widening of the center part, or scalp irritation. When these signs and changes occur, they must be taken seriously, and immediate medical attention should be sought.
——- Ad ——-
——- Ad ——-
Types of Hair Loss
Hair loss in humans presents in three different patterns:
* Androgenetic Alopecia: This is a hereditary condition that affects both genders and is the most common cause of hair loss in women, impacting hundreds of millions worldwide. This type of hair loss is characterized by a gradual shrinking (miniaturization) of hair follicles, which stops their growth, especially on the top and sides of the scalp, leading to thinning in these areas.
* Anagen Effluvium: This pattern results from treatments known to damage hair follicles, such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer. Here, hair falls out within a few weeks of starting treatment and typically regrows a few months after the sessions are completed.
* Telogen Effluvium: This occurs when an excessive number of hair follicles prematurely enter the final (resting) phase of the hair growth cycle. This type of hair loss is attributed to several causes, including certain illnesses, medications, hormonal fluctuations, and psychological or physical stress.
What Medical Conditions Cause Hair Loss in Women?
Below is a list of diseases implicated in hair loss among women:
* Anemia: Hair loss is a primary symptom of anemia, especially in women. This results from a reduced number of red blood cells reaching the hair follicles to supply them with oxygen and nutrients.
* Diabetes Mellitus: Fluctuations in blood sugar levels and other associated symptoms can lead to brittle hair and subsequent shedding. Specifically, chronic high blood sugar can damage the small blood vessels that nourish the hair follicles, weakening the hair and limiting its growth.
* Thyroid Disorders: This gland plays a prominent role in regulating hair growth. Hair structure can be compromised if thyroid hormone levels are imbalanced, whether they are too high (hyperthyroidism) or too low (hypothyroidism).
* Psychological Crises like Anxiety and Depression: The common factor in these disorders is stress. As mentioned earlier, stress contributes to hair loss. The hair loss itself can also be a source of stress, creating a vicious cycle for the patient.
* Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): This is a hormonal disorder caused by an increase in male hormone (androgen) activity in women, which can result in hair thinning, particularly at the front of the scalp.
* Dermatological Diseases: These include Tinea Capitis (scalp ringworm), Psoriasis, Seborrheic Dermatitis, and Scarring Alopecia.
Other Common Causes of Hair Loss in Women
Simultaneously, certain behaviors, habits, and circumstances can lead to hair loss in women, including:
* Smoking: Hair loss is another charge laid against cigarettes, as tobacco contributes to damaging hair follicles and impeding blood flow to the scalp.
* Pregnancy and Childbirth: The prevailing hormonal changes can cause excessive hair shedding, especially in the postpartum period, which can last for up to six months.
* Unhealthy Diet: Naturally, when hair does not receive the necessary nutrients, its structure erodes and weakens. Key nutrients for hair health include vitamin A, iron, zinc, and B vitamins (especially B7 and B12).
* Improper Hair Care: This can involve aggressive styling with excessive heat or pulling the hair too tightly. This practice is associated with a condition called “Traction Alopecia.”
Risk Factors:
- Aging
- Menopause
- Chemotherapy and radiation therapy
- A family history of hair loss
——- Ad ——-
——- Ad ——-
How is Hair Loss Diagnosed?
If you notice persistent or rapid thinning, widening of the part, or bald patches, see a dermatologist early diagnosis widens your treatment options.
There are several tests used to evaluate hair loss:
* Pull Test: The doctor gently pulls a small bundle of about 60 hairs to measure the amount of shedding. If more than 10% of the pulled hairs come out (approximately 6 or more), this indicates a positive result and that you are suffering from pathological hair loss.
* Standardized Wash Test: The patient is asked not to shampoo their hair for five consecutive days. Afterward, they wash and rinse it with warm water in a basin with its drain covered by gauze. The collected hairs are then sent for examination to count their number and length and to determine the pattern of hair loss.
* Blood Tests: The purpose of this test is to rule out any underlying health conditions that could lead to hair loss, such as thyroid disorders. It can also be used to determine levels of essential nutrients for hair health, like iron and zinc.
* Trichogram: This test is used to evaluate the condition of the hair from its roots. It is a semi-invasive microscopic method where a group of hairs (60-80) is plucked from two different areas of the scalp. The hairs are removed with forceps and immediately placed on a glass slide under a microscope or magnifying lens to study the percentage of hairs in each phase of the growth cycle.
* Videodermoscopy: A technique used for diagnosing pigmented lesions, it has recently been adopted for hair examinations. This tool provides precise imaging of the scalp and hair, even visualizing the hair shaft within the follicle (if present) to show its diameter, length, and any underlying abnormalities.
* Scalp Biopsy: This is a diagnostic procedure where a small skin sample is removed. The doctor resorts to this in ambiguous cases, especially when it is necessary to differentiate between scarring and non-scarring alopecia.
What is the Treatment for Hair Loss?
The good news is that a variety of innovative treatments for hair loss exist. The type of treatment depends on the underlying cause:
1. Medications
* Minoxidil (Rogaine): This is a topical solution applied directly to the scalp. Its function is to open potassium channels in cells, which results in vasodilation (widening of blood vessels), creating a favorable environment for hair follicles to grow during the anagen (growth) phase of the hair cycle.
It is an effective treatment for both genders and is approved for women to treat androgenetic alopecia. This medication does not require a prescription, and the active ingredient is available in 2% and 5% concentrations.
* Prescription Oral Medications: These include prostaglandins, spironolactone, ketoconazole, melatonin, and finasteride. However, the effect of finasteride in women is weak, and it is not FDA-approved for female pattern hair loss. Pregnant and breastfeeding women are strictly prohibited from taking finasteride due to its risk to the development of a male fetus and its male sexual characteristics.
2. Microneedling
This is a minimally invasive dermatological procedure where a specialist uses very fine needles to puncture the scalp. This procedure is often combined with adjuvant hair growth treatments such as minoxidil, Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP), and corticosteroid creams. It stimulates collagen production in the scalp, promotes neovascularization (formation of new blood vessels), and enhances blood flow to the affected area.
3. Hair Transplantation
Hair transplantation is not just for men; women also undergo this procedure for hair loss. It is a viable option for female patients over 25 who suffer from severe hair loss and have not responded to medical treatments. Women wishing to undergo the procedure must have dense hair in the donor area (the occipital region at the back of the head).
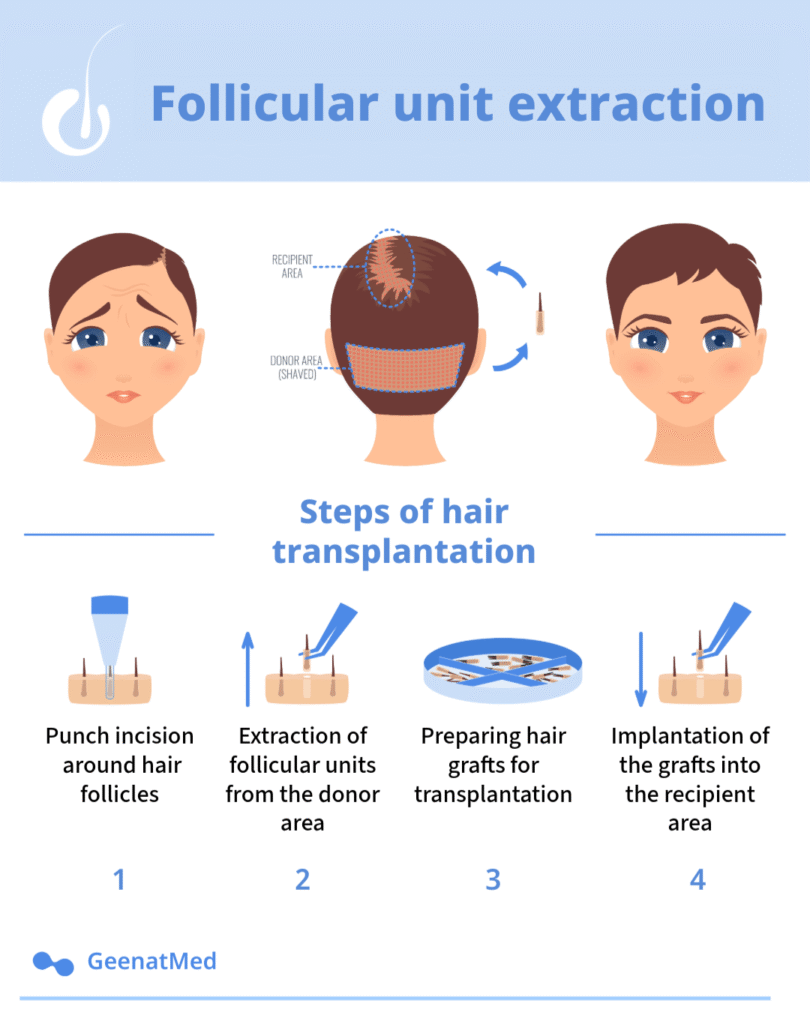
The most famous hair transplant technique is Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). In this method, the donor area at the back of the head is shaved. Then, a circular incision is made around the hair follicles with a punch tool to separate them from their tissue, allowing them to be extracted one by one with forceps and stored in a special solution in preparation for transplantation.
After collection, the extracted follicles are implanted into the recipient (bald) areas. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia of the scalp. In a single session, hundreds to a few thousand grafts (each graft containing 1 to 4 hairs) are implanted.
4. Light Therapies
These include Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT), which aims to stimulate hair growth and increase its density. Despite the debate surrounding its effectiveness in treating hair loss, several forms of LLLT devices have been introduced to the market, including combs, helmets, and caps.
——- Ad ——-
——- Ad ——-
How Can I Care for My Hair and Prevent It from Falling Out?
To care for your hair and prevent shedding, you must provide it with a healthy lifestyle. We recommend applying the following health guidelines:
* Follow a Balanced Diet: Be sure to eat foods rich in protein (like chicken, fish, and eggs), as hair is primarily composed of protein. Also, include sources of iron (like spinach, pasta, and liver), and consume foods containing other hair-friendly nutrients such as biotin, vitamin D, and vitamin A (note: excessive intake of vitamin A can lead to toxicity).
* Use Products Suited to Your Hair Type: Choose a shampoo and conditioner appropriate for your hair and scalp type, and wash your hair two to three times a week with lukewarm water. Some hair types may benefit from sulfate-free and silicone-free products.
* Style Your Hair Gently: Avoid tight hairstyles such as tight braids, a tight bun, or a very high ponytail, which can lead to hair loss. Instead, opt for comfortable and safe styles that are free from tight pulling.
* Manage Your Stress Gently: As mentioned earlier, stress is a contributing factor to hair loss in women. Therefore, it is essential to manage feelings of stress and strain. To do this, engage in exercise and relaxation techniques (like yoga), and drink the recommended amount of water throughout the day to hydrate your body and hair cells. End your day by sleeping at a specific, early time, and enjoy 7-8 hours of rest, giving your body’s cells a chance to regenerate.
Conclusion
Hair is not merely an aesthetic feature; it is also an indicator of our general health and a body free from disease. Radiant hair is the result of practicing positive habits that promote its health and longevity. By adhering to proper hair care routines, we can cultivate beneficial practices and boast truly flawless, undamaged hair.
○ Share the article:
References
(1) Fabbrocini, G., Cantelli, M., Masarà, A., Annunziata, M. C., Marasca, C., & Cacciapuoti, S. (2018). Female pattern hair loss: A clinical, pathophysiologic, and therapeutic review. International journal of women’s dermatology, 4(4), 203–211.
(2) Kelly Bilodeau (2024), Thinning hair in women: Why it happens and what helps, Harvard Health Publishing. Retrieved on 3 July, 2025
(3) What causes female hair loss? (2023), UCLA Health, Retrieved on 3 July, 2025
(4) Hair loss, NHS, Retrieved on 3 July, 2025

